A gear is a rotating circular part with teeth that engage with the teeth of another gear in order to change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source by rotational motion.
When designing a gear, there are several necessary parameters that need to be considered. The specific parameters may vary depending on the type of gear and the application, but here are some fundamental ones to consider:
1. Gear Type:
Determine the type of gear you want to design, such as spur gear, helical gear, bevel gear, worm gear, etc. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications.
2. Module or Pitch
Module is used for metric gears, while pitch is used for imperial gears. It defines the size of the gear teeth and the spacing between them. The module or pitch value is crucial for gear design and influences other parameters.
3. Number of Teeth
The number of teeth determines the gear ratio and affects the gear’s size and strength. The number of teeth should be selected based on the desired gear ratio and application requirements.
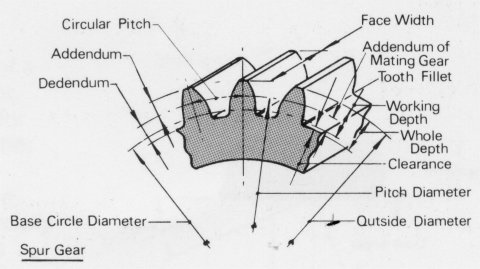
4. Dimensions of the gear
The dimensions of a gear depend on several factors, including the gear type, module or pitch, number of teeth, and specific design requirements. Here are some key dimensions commonly associated with gears:
- Pitch Diameter
- Outside Diameter
- Root Diameter
- Addendum
- Dedendum
- Tooth Thickness
- Tooth Depth
- Face Width
5. Pressure Angle
The pressure angle determines the tooth profile and influences the gear’s load-carrying capacity, efficiency, and smoothness of operation.
6. Profile Shift
Profile shift is the modification made to the tooth profile to adjust the gear’s performance characteristics. It affects factors like gear meshing, backlash, and contact ratio. Profile shift can be positive, negative, or zero.
7. Material Selection
Choose an appropriate material based on the gear’s application, operating conditions, and required strength. Common gear materials include steel, cast iron, bronze, and various alloys.
8. Manufacturing Method
Determine the manufacturing method for producing the gear, such as milling, hobbing, shaping, or 3D printing. The chosen method may impact the design and tolerances.

9. Accuracy and Tolerance
Define the required accuracy and tolerance levels for the gear’s dimensions and tooth profile. This influences the manufacturing process and the gear’s performance.
These parameters provide a foundation for gear design. However, it’s important to note that gear design can be complex and requires in-depth knowledge and expertise. Consulting gear design standards or working with experienced gear designers can help ensure accurate and reliable gear designs for specific applications.
You can find the photo display of the CNC machining parts made by us HERE!